...
Overview
...
Package: wireless
RouterOS wireless comply complies with IEEE 802.11 standards, it provides complete support for 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n and 802.11ac as long as additional features like WPA, WEP, AES encryption, Wireless Distribution System (WDS), Dynamic Frequency selection (DFS), Virtual Access Point, Nstreme and NV2 proprietary protocols and many more. Wireless features compatibility table for different wireless protocols.
...
Sub-menu: /interface wireless
| Property | Description |
|---|
| adaptive-noise-immunity |
| (ap-and-client-mode | client-mode | none; Default: |
| none) | This property is only effective for cards based on Atheros chipset. |
| allow-sharedkey |
| no) | Allow WEP Shared Key clients to connect. Note that no authentication is done for these clients (WEP Shared keys are not compared to anything) - they are just accepted at once (if access list allows that) |
| ampdu-priorities |
| (list of integer [0..7]; Default: |
| 0) | Frame priorities for which AMPDU sending (aggregating frames and sending using block acknowledgment) should get negotiated and used. Using AMPDUs will increase throughput, but may increase latency, therefore, may not be desirable for real-time traffic (voice, video). Due to this, by default AMPDUs are enabled only for best-effort traffic. |
| amsdu-limit |
| (integer [0..8192]; Default: |
| 8192) | Max AMSDU that device is allowed to prepare when negotiated. AMSDU aggregation may significantly increase throughput especially for small frames, but may increase latency in case of packet loss due to retransmission of aggregated frame. Sending and receiving AMSDUs will also increase CPU usage. |
| amsdu-threshold |
| (integer [0..8192]; Default: |
| 8192) | Max frame size to allow including in AMSDU. |
| antenna-gain |
| (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: |
| 0) | Antenna gain in dBi, used to calculate maximum transmit power according to |
| (ant-a | ant-b | rxa-txb | txa-rxb; Default: ) | Select antenna to use for transmitting and for receiving |
- - use only 'a' antenna
- ant-b
|
- - use only 'b' antenna
- txa-rxb
|
- - use antenna 'a' for transmitting, antenna 'b' for receiving
- rxa-txb
|
- - use antenna 'b' for transmitting, antenna 'a' for receiving
|
| area |
| (string; Default: ) | Identifies group of wireless networks. This value is announced by AP, and can be matched in |
| area-prefix. This is a proprietary extension. |
| arp |
| (disabled | enabled | proxy-arp | reply-only; Default: |
| (auto | integer; Default: |
| auto) | ARP timeout is time how long ARP record is kept in ARP table after no packets are received from IP. Value |
| /ip settings, default is 30s |
| band |
| (2ghz-b | 2ghz-b/g | 2ghz-b/g/n | 2ghz-onlyg | 2ghz-onlyn | 5ghz-a | 5ghz-a/n | 5ghz-onlyn | 5ghz-a/n/ac | 5ghz- |
only| onlyac | 5ghz-n/ac; Default: ) | Defines set of used data rates, channel frequencies and widths. |
| basic-rates-a/g |
| (12Mbps | 18Mbps | 24Mbps | 36Mbps | 48Mbps | 54Mbps | 6Mbps | 9Mbps; Default: |
| property, but used for 5ghz, 5ghz-10mhz, 5ghz-5mhz, 5ghz-turbo, 2.4ghz-b/g, 2.4ghz-onlyg, 2ghz-10mhz, 2ghz-5mhz and 2.4ghz-g-turbo bands. |
| basic-rates-b |
| (11Mbps | 1Mbps | 2Mbps | 5.5Mbps; Default: |
| 1Mbps) | List of basic rates, used for 2.4ghz-b, 2.4ghz-b/g and 2.4ghz-onlyg bands. Client will connect to AP only if it supports all basic rates announced by the AP. AP will establish WDS link only if it supports all basic rates of the other AP. This property has effect only in AP modes, and when value of |
| is configured. |
| bridge-mode |
| (disabled | enabled; Default: |
| enabled) | Allows to use station-bridge mode. |
| (integer | disabled; Default: |
| disabled) | Time in microseconds which will be used to send data without stopping. Note that no other wireless cards in that network will be able to transmit data during burst-time microseconds. This setting is available only for AR5000, AR5001X, and AR5001X+ chipset based cards. |
| channel-width |
| (20/40/80/160mhz-Ceeeeeee | 20/40/80/160mhz-XXXXXXXX | 20/40/80/160mhz-eCeeeeee | 20/40/80/160mhz-eeCeeeee | 20/40/80/160mhz-eeeCeeee | 20/40/80/160mhz-eeeeCeee | 20/40/80/160mhz-eeeeeCee | 20/40/80/160mhz-eeeeeeCe | 20/40/80/160mhz-eeeeeeeC | 20/40/80mhz-Ceee | 20/40/80mhz-eCee | 20/40/80mhz-eeCe | 20/40/80mhz-eeeC | 20/40/80mhz-XXXX | 20/40mhz-Ce | 20/40mhz-eC | 20/40mhz-XX | 40mhz-turbo | 20mhz | 10mhz | 5mhz; Default: |
| 20mhz) | Use of extension channels (e.g. Ce, eC etc) allows additional 20MHz extension channels and if it should be located below or above the control (main) channel. Extension channel allows 802.11n devices to use up to 40MHz (802.11ac up to 160MHz) of spectrum in total thus increasing max throughput. Channel widths with XX and XXXX extensions automatically scan for a less crowded control channel frequency based on the number of concurrent devices running in every frequency and chooses the “C” - Control channel frequency automatically. |
| comment |
| (string; Default: ) | Short description of the interface |
| compression |
| no) | Setting this property to |
| will allow the use of the hardware compression. Wireless interface must have support for hardware compression. Connections with devices that do not use compression will still work. |
| country |
| (name of the country | no_country_set; Default: |
no_country_set| etsi) | Limits available bands, frequencies and maximum transmit power for each frequency. Also specifies default value of |
| is an FCC compliant set of channels. |
| default-ap-tx-limit |
| (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: |
| for clients that do not match any entry in the |
| yes) | For AP mode, this is the value of |
| for clients that do not match any entry in the |
| for APs that do not match any entry in the |
| (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: |
| for clients that do not match any entry in the |
| for clients that do not match any entry in the |
| interface will always have running flag. If value is set to |
| no', the router determines whether the card is up and running - for AP one or more clients have to be registered to it, for station, it should be connected to an AP. |
| disabled |
| yes) | Whether interface is disabled |
| disconnect-timeout |
| (time [0s..15s]; Default: |
| 3s) | This interval is measured from third sending failure on the lowest data rate. At this point 3 * (hw-retries |
| + 1) frame transmits on the lowest data rate had failed. During |
| packet transmission will be retried with |
diconnect| interval. If no frame can be transmitted successfully during |
| disconnect-timeout, the connection is closed, and this event is logged as "extensive data loss". Successful frame transmission resets this timer. |
| distance |
| (integer | dynamic | indoors; Default: |
| dynamic) | How long to wait for confirmation of unicast frames (ACKs) before considering transmission unsuccessful |
. Value 'dynamic' , or in short ACK-Timeout. Distance value has these behaviors:- Dynamic - causes AP to detect and use the smallest timeout that works with all connected clients.
|
Acknowledgments are not used in Nstreme protocol.- Indoor - uses the default ACK timeout value that the hardware chip manufacturer has set.
- Number - uses the input value in formula: ACK-timeout = ((distance * 1000) + 299) / 300 us;
Acknowledgments are not used in Nstreme/NV2 protocols. |
| frame-lifetime |
frame-lifetime | (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: |
| 0) | Discard frames that have been queued for sending longer than |
| frame-lifetime. By default, when value of this property is |
| 0, frames are discarded only after connection is closed. |
| frequency |
| (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: ) | Channel frequency value in MHz on which AP will operate. Allowed values depend on the selected band, and are restricted by |
setting and wireless card capabilities. This setting has |
if interface is in any of |
mode, or if DFS is active. Note: If using mode "superchannel", any frequency supported by the card will be accepted, but on the RouterOS client, any non-standard frequency must be configured in the |
| scan-list, otherwise it will not be scanning in non-standard range. In Winbox, scanlist frequencies are in |
| bold, any other frequency means the clients will need scan-list configured. |
| frequency-mode |
| (manual-txpower | regulatory-domain | superchannel; Default: |
manual-txpower| regulatory_domain) | Three frequency modes are available: |
- - Limit available channels and maximum transmit power for each channel according to the value of
|
- - Same as above, but do not limit maximum transmit power.
- superchannel
|
- - Conformance Testing Mode. Allow all channels supported by the card.
List of available channels for each band can be seen in |
| /interface wireless info allowed-channels. This mode allows you to test wireless channels outside the default scan-list and/or regulatory domain. This mode should only be used in controlled environments, or if you have |
a | special permission to use it in your region. Before v4.3 this was called Custom Frequency Upgrade, or Superchannel. Since RouterOS v4.3 this mode is available without special key upgrades to all installations. |
| frequency-offset |
| (integer [-2147483648..2147483647]; Default: |
| 0) | Allows to specify offset if the used wireless card operates at a different frequency than is shown in RouterOS, in case a frequency converter is used in the card. So if your card works at 4000MHz but RouterOS shows 5000MHz, set offset to 1000MHz and it will be displayed correctly. The value is in MHz and can be positive or negative. |
| guard-interval |
| any) | Whether to allow use of short guard interval (refer to 802.11n MCS specification to see how this may affect throughput). "any" will use either short or long, depending on data rate, "long" will use long. |
| hide-ssid |
- - AP does not include SSID in the beacon frames, and does not reply to probe requests that have broadcast SSID.
- no
|
- - AP includes SSID in the beacon frames, and replies to probe requests that have broadcast SSID.
This property has an effect only in AP mode. Setting it to |
| can remove this network from the list of wireless networks that are shown by some client software. Changing this setting does not improve the security of the wireless network, because SSID is included in other frames sent by the AP. |
| ht-basic-mcs |
| (list of (mcs-0 | mcs-1 | mcs-2 | mcs-3 | mcs-4 | mcs-5 | mcs-6 | mcs-7 | mcs-8 | mcs-9 | mcs-10 | mcs-11 | mcs-12 | mcs-13 | mcs-14 | mcs-15 | mcs-16 | mcs-17 | mcs-18 | mcs-19 | mcs-20 | mcs-21 | mcs-22 | mcs-23); Default: |
| that every connecting client must support. Refer to 802.11n for MCS specification. |
| ht-supported-mcs |
| (list of (mcs-0 | mcs-1 | mcs-2 | mcs-3 | mcs-4 | mcs-5 | mcs-6 | mcs-7 | mcs-8 | mcs-9 | mcs-10 | mcs-11 | mcs-12 | mcs-13 | mcs-14 | mcs-15 | mcs-16 | mcs-17 | mcs-18 | mcs-19 | mcs-20 | mcs-21 | mcs-22 | mcs-23); Default: |
| mcs-0; mcs-1; mcs-2; mcs-3; mcs-4; mcs-5; mcs-6; mcs-7; mcs-8; mcs-9; mcs-10; mcs-11; mcs-12; mcs-13; mcs-14; mcs-15; mcs-16; mcs-17; mcs-18; mcs-19; mcs-20; mcs-21; mcs-22; mcs-23) | Modulation and Coding Schemes |
| that this device advertises as supported. Refer to 802.11n for MCS specification. |
| hw-fragmentation-threshold |
| (integer[256..3000] | disabled; Default: |
| 0) | Specifies maximum fragment size in bytes when transmitted over the wireless medium. 802.11 standard packet (MSDU in 802.11 |
terminology| terminologies) fragmentation allows packets to be fragmented before transmitting over a wireless medium to increase the probability of successful transmission (only fragments that did not transmit correctly are retransmitted). Note that transmission of a fragmented packet is less efficient than transmitting unfragmented packet because of protocol overhead and increased resource usage at both - transmitting and receiving party. |
| hw-protection-mode |
| (cts-to-self | none | rts-cts; Default: |
| none) | Frame protection support property |
| (integer [0..65535]; Default: |
| 0) | Frame protection support property |
| (integer [0..15]; Default: |
| 7) | Number of times sending frame is retried without considering it a transmission failure. Data-rate is decreased upon failure and the frame is sent again. Three sequential failures on the lowest supported rate suspend transmission to this destination for the duration of |
| on-fail-retry-time. After that, the frame is sent again. The frame is being retransmitted until transmission success, or until the client is disconnected after |
Frame | The frame can be discarded during this time if |
| (any | indoor | outdoor; Default: |
| any) | Adjusts scan-list to use indoor, outdoor or all frequencies for the country that is set. |
| interworking-profile |
| (enabled | disabled; Default: |
| disabled) |
|
| keepalive-frames |
| (enabled | disabled; Default: |
l2mtu (integer [0..Applies only if wireless interface is in mode=ap-bridge. If a client has not communicated for around 20 seconds, AP sends a "keepalive-frame".
Note, disabling the feature can lead to "ghost" clients in registration-table. |
| l2mtu (integer [0..65536]; Default: |
| (MAC; Default: ) |
|
| master-interface |
| (string; Default: ) | Name of wireless interface that has |
| interface will only work if master interface is in |
| mode. This property is only for virtual AP interfaces. |
| max-station-count |
| (integer [1..2007]; Default: |
| 2007) | Maximum number of associated clients. WDS links also count toward this limit. |
| mode |
| (station | station-wds | ap-bridge | bridge | alignment-only | nstreme-dual-slave | wds-slave | station-pseudobridge | station-pseudobridge-clone | station-bridge; Default: |
| station) | Selection between different station and access point (AP) modes. Station modes: |
- - Basic station mode. Find and connect to acceptable AP.
- station-wds
|
- station, but create WDS link with AP, using proprietary extension. AP configuration has to allow WDS links with this device. Note that this mode does not use entries in
|
- station, but additionally perform MAC address translation of all traffic. Allows interface to be bridged.
- station-pseudobridge-clone
|
- station-pseudobridge, but use
|
- address to connect to AP.
- station-bridge - Provides support for transparent protocol-independent L2 bridging on the station device. RouterOS AP accepts clients in station-bridge mode when enabled using bridge-mode parameter. In this mode, the AP maintains a forwarding table with information on which MAC addresses are reachable over which station device. Only works with RouterOS APs. With station-bridge mode, it is not possible to connect to CAPsMAN controlled CAP.
AP modes: |
- - Basic access point mode.
- bridge
|
- ap-bridge, but limited to one associated client.
- wds-slave
|
- ap-bridge, but scan for AP with the same
|
- and establishes WDS link. If this link is lost or cannot be established, then continue scanning. If
|
- radar-detect, then APs with enabled
|
- will not be found during scanning.
Special modes: |
- - Put the interface in a continuous transmit mode that is used for aiming the remote antenna.
- nstreme-dual-slave
|
- - allow this interface to be used in nstreme-dual setup.
MAC address translation |
in pseudobridge modes in pseudobridge modes works by inspecting packets and building a table of corresponding IP and MAC addresses. All packets are sent to AP with the MAC address used by pseudobridge, and MAC addresses of received packets are restored from the address translation table. There is a single entry in the address translation table for all non-IP packets, hence more than one host in the bridged network cannot reliably use non-IP protocols. Note: Currently IPv6 doesn't work over Pseudobridge |
| mtu |
| (integer [0..65536]; Default: |
| (disabled | enabled; Default: |
| enabled) | For a client that has power saving, buffer multicast packets until next beacon time. A client should wake up to receive a beacon, by receiving beacon it sees that there are multicast packets pending, and it should wait for multicast packets to be sent. |
| multicast-helper |
| (default | disabled | full; Default: |
| default) | When set to full, multicast packets will be sent with a unicast destination MAC address, resolving |
| on the wireless link. This option should be enabled only on the access point, clients should be configured in |
mode. Available starting from v5.15.- disabled - disables the helper and sends multicast packets with multicast destination MAC addresses
- dhcp - dhcp packet mac addresses are changed to unicast mac addresses prior to sending them out
- full - all multicast packet mac address are changed to unicast mac addresses prior to sending them out
- default - default choice that currently is set to
|
disabled- dhcp. Value can be changed in future releases.
|
| name |
| (string; Default: ) | name of the interface |
| noise-floor-threshold |
| (default | integer [-128..127]; Default: |
| default) | For advanced use only, as it can badly affect the performance of the interface. It is possible to manually set noise floor threshold value. By default, it is dynamically calculated. This property also affects received signal strength. This property is only effective on non-AC chips. |
| nv2-cell-radius |
| (integer [10..200]; Default: |
| 30) | Setting affects the size of contention time slot that AP allocates for clients to initiate connection and also size of time slots used for estimating distance to client. When setting is too small, clients that are farther away may have trouble connecting and/or disconnect with "ranging timeout" error. Although during normal operation the effect of this setting should be negligible, in order to maintain maximum performance, it is advised to not increase this setting if not necessary, so AP is not reserving time that is actually never used, but instead allocates it for actual data transfer.- on AP: distance to farthest client in km
- on station: no effect
|
| nv2-noise-floor-offset |
| (default | integer [0..20]; Default: |
| default) |
|
| nv2-preshared-key |
| (string; Default: ) |
|
| nv2-qos |
| (default | frame-priority; Default: |
| default) | Sets the packet priority mechanism, firstly data from high priority queue is sent, then lower queue priority data until 0 queue priority is reached. When link is full with high priority queue data, lower priority data is not sent. Use it very carefully, setting works on AP |
- - manual setting that can be tuned with Mangle rules.
- default
|
- - default setting where small packets receive priority for best latency
|
| nv2-queue-count |
| (integer [2..8]; Default: |
| (disabled | enabled; Default: |
| disabled) |
|
| on-fail-retry-time |
| (time [100ms..1s]; Default: |
| 100ms) | After third sending failure on the lowest data rate, wait for specified time interval before retrying. |
| periodic-calibration |
| (default | disabled | enabled; Default: |
| enables periodic calibration if |
| default-periodic-calibration |
| enabled. Value of that property depends on the type of wireless card. This property is only effective for cards based on Atheros chipset. |
| periodic-calibration-interval |
| (integer [1..10000]; Default: |
| 60) | This property is only effective for cards based on Atheros chipset. |
| preamble-mode |
| (both | long | short; Default: |
| both) | Short preamble mode is an option of 802.11b standard that reduces per-frame overhead. |
- - Do not use short preamble.
- short
|
- - Announce short preamble capability. Do not accept connections from clients that do not have this capability.
- both
|
- - Announce short preamble capability.
- On station:
|
- - do not use short preamble.
- short
|
- - do not connect to AP if it does not support short preamble.
- both
|
- - Use short preamble if AP supports it.
|
| prism-cardtype |
| (100mW | 200mW | 30mW; Default: ) | Specify type of the installed Prism wireless card. |
| proprietary-extensions |
| (post-2.9.25 | pre-2.9.25; Default: |
| post-2.9.25) | RouterOS includes proprietary information in an information element of management frames. This parameter controls how this information is included. |
- - This is older method. It can interoperate with newer versions of RouterOS. This method is incompatible with some clients, for example, Centrino based ones.
- post-2.9.25
|
- - This uses standardized way of including vendor specific information, that is compatible with newer wireless clients.
|
| radio-name |
| MAC address of an interface) | Descriptive name of the device, that is shown in registration table entries on the remote devices. This is a proprietary extension. |
| rate-selection |
| (advanced | legacy; Default: |
| advanced) | Starting from v5.9 default value is advanced since legacy mode was inefficient. |
| rate-set |
| (configured | default; Default: |
| default) | Two options are available: |
- - default basic and supported rate sets are used. Values from
|
- parameters have no effect.
- configured
|
| (list of integer [0..3]; Default: |
| 0) | Which antennas to use for receive. In current MikroTik routers, both RX and TX chain must be enabled, for the chain to be enabled. |
scan-list (Comma separated list of frequencies and frequency ranges | default. Since v6.35 (wireless-rep) type also support range:step option; Default: |
| value is all channels from selected band that are supported by card and allowed by the |
| settings (this list can be seen in |
| info). For default scan list in |
| band channels are taken with 20MHz step, in |
| band - with 40MHz step, for all other bands - with 5MHz step. If |
| is specified manually, then all matching channels are taken. (Example: |
| scan-list=default,5200-5245,2412-2427 |
| - This will use the default value of scan list for current band, and add to it supported frequencies from 5200-5245 or 2412-2427 range.) |
Since RouterOS v6.0 with Winbox or Webfig, for inputting of multiple frequencies, add each frequency or range of frequencies into separate multiple scan-lists. Using a comma to separate frequencies is no longer supported in Winbox/Webfig since v6.0. Since RouterOS v6.35 (wireless-rep) scan-list support step feature where it is possible to manually specify the scan step. Example: |
| scan-list=5500-5600:20 will generate such scan-list values |
| 5500,5520,5540,5560,5580,5600 |
| security-profile |
| default) | Name of profile from |
ssid (string (0..32 chars); Default: value of | secondary-channel (integer; Default: "") | Specifies secondary channel, required to enable 80+80MHz transmission. To disable 80+80MHz functionality, set secondary-channel to "" or unset the value via CLI/GUI. |
| ssid (string (0..32 chars); Default: value of system/identity) | SSID (service set identifier) is a name that identifies wireless network. |
| skip-dfs-channels (string | 10min-cac | all | disabled; Default: disabled) | These values are used to skip all DFS channels or specifically skip DFS CAC channels in range 5600-5650MHz which detection could go up to 10min. |
| station-bridge-clone-mac |
| (MAC; Default: ) | This property has effect only in the |
| station-pseudobridge-clone |
| mode. Use this MAC address when connection to AP. If this value is |
00:00:00:00:00:00, station will initially use MAC address of the wireless interface. As soon as packet with MAC address of another device needs to be transmitted, station will reconnect to AP using that address. |
| station-roaming |
| (disabled | enabled; Default: |
enabled| disabled) | Station Roaming feature is available only for 802.11 wireless protocol and only for station modes. |
| (list of rates [12Mbps | 18Mbps | 24Mbps | 36Mbps | 48Mbps | 54Mbps | 6Mbps | 9Mbps]; Default: |
| 6Mbps; 9Mbps; 12Mbps; 18Mbps; 24Mbps; 36Mbps; 48Mbps; 54Mbps) | List of supported rates, used for all bands except |
| (list of rates [11Mbps | 1Mbps | 2Mbps | 5.5Mbps]; Default: |
| 1Mbps; 2Mbps; 5.5Mbps; 11Mbps) | List of supported rates, used for |
| bands. Two devices will communicate only using rates that are supported by both devices. This property has effect only when value of |
| configured. |
| tdma-period-size |
| (integer [1..10]; Default: |
| 2) | Specifies TDMA period in milliseconds. It could help on the longer distance links, it could slightly increase bandwidth, while latency is increased too. |
| tx-chains |
| (list of integer [0..3]; Default: |
| 0) | Which antennas to use for transmitting. In current MikroTik routers, both RX and TX chain must be enabled, for the chain to be enabled. |
| tx-power |
30| 40]; Default: ) | For 802.11ac wireless interface it's total power but for 802.11a/b/g/n it's power per chain. |
| tx-power-mode |
| (default, card-rates, all- |
rated| rates-fixed, manual-table; Default: |
| default) | sets up tx-power mode for wireless card- default - use values stored in the card
|
card use transmit power as defined by tx-power settingall-rated-- fixed - use same transmit power for all data rates. Can damage the card if transmit power is set above rated value of the card for used rate.
- manual-table - define transmit power for each rate separately. Can damage the card if transmit power is set above rated value of the card for used rate.
|
update-- card-rates - use transmit power calculated for each rate based on value of tx-power parameter. Legacy mode only compatible with currently discontinued products.
|
| update-stats-interval |
| (; Default: ) | How often to request update of signals strength and ccq values from clients. Access to |
also triggers update of these values. This is proprietary extension. |
| vht-basic-mcs |
| (none | MCS 0-7 | MCS 0-8 | MCS 0-9; Default: |
| that every connecting client must support. Refer to 802.11ac for MCS specification. You can set MCS interval for each of Spatial Stream |
- - will not use selected Spatial Stream
- MCS 0-7
|
- - client must support MCS-0 to MCS-7
- MCS 0-8
|
- - client must support MCS-0 to MCS-8
- MCS 0-9
|
- - client must support MCS-0 to MCS-9
|
| vht-supported-mcs |
| (none | MCS 0-7 | MCS 0-8 | MCS 0-9; Default: |
| that this device advertises as supported. Refer to 802.11ac for MCS specification. You can set MCS interval for each of Spatial Stream |
- - will not use selected Spatial Stream
- MCS 0-7
|
- - devices will advertise as supported MCS-0 to MCS-7
- MCS 0-8
|
- - devices will advertise as supported MCS-0 to MCS-8
- MCS 0-9
|
- - devices will advertise as supported MCS-0 to MCS-9
|
| wds-cost-range |
04294967295 | 50-150) | Bridge port cost of WDS links are automatically adjusted, depending on measured link throughput. Port cost is recalculated and adjusted every 5 seconds if it has changed by more than 10%, or if more than 20 seconds have passed since the last adjustment. Setting this property to |
disables automatic cost adjustment. Automatic adjustment does not work for WDS links that are manually configured as a bridge port. |
| wds-default-bridge |
| none) | When WDS link is established and status of the wds interface becomes |
| running, it will be added as a bridge port to the bridge interface specified by this property. When WDS link is lost, wds interface is removed from the bridge. If wds interface is already included in a bridge setup when WDS link becomes active, it will not be added to bridge specified by , and will |
| (needs editing) |
| wds-default-cost |
04294967295 | 100) | Initial bridge port cost of the WDS links. |
| wds-ignore-ssid |
| no) | By default, WDS link between two APs can be created only when they work on the same frequency and have the same SSID value. If this property is set to |
| yes, then SSID of the remote AP will not be checked. This property has no effect on connections from clients in |
| mode. It also does not work if |
| (disabled | dynamic | dynamic-mesh | static | static-mesh; Default: |
| disabled) | Controls how WDS links with other devices (APs and clients in |
- does not allow WDS links.
- static
|
- only allows WDS links that are manually configured in
|
wds - also allows WDS links with devices that are not configured in
|
wds- WDS, by creating required entries dynamically. Such dynamic WDS entries are removed automatically after the connection with the other AP is lost.
- |
mesh modes mesh modes use different (better) method for establishing link between AP, that is not compatible with APs in non-mesh mode. This method avoids one-sided WDS links that are created only by one of the two APs. Such links cannot pass any data.When AP or station is establishing WDS connection with another AP, it |
uses connectlist to list to check whether this connection is allowed. If station |
in stationwds mode wds mode is establishing connection with AP, AP |
uses accesslist to list to check whether this connection is allowed. |
If mode is stationIf mode is station-wds, then this property has no effect. |
| wireless-protocol |
| (802.11 | any | nstreme | nv2 | nv2-nstreme | nv2-nstreme-802.11 | unspecified; Default: |
unspecified| any) | Specifies protocol used on wireless interface; |
- - protocol mode used on previous RouterOS versions (v3.x, v4.x). Nstreme is enabled by old enable-nstreme setting, Nv2 configuration is not possible.
- any : on AP - regular 802.11 Access Point or Nstreme Access Point; on station - selects Access Point without specific sequence, it could be changed by connect-list rules.
- nstreme
|
- - enables Nstreme protocol (the same as old enable-nstreme setting).
- nv2
|
- - enables Nv2 protocol.
- nv2 nstreme : on AP - uses first wireless-protocol setting, always Nv2; on station - searches for Nv2 Access Point, then for Nstreme Access Point.
- nv2 nstreme 802.11
|
- - on AP - uses first wireless-protocol setting, always Nv2; on station - searches for Nv2 Access Point, then for Nstreme Access Point, then for regular 802.11 Access Point.
Warning! |
| Nv2 doesn't have support for Virtual AP |
| wmm-support |
| (disabled | enabled | required; Default: |
| disabled) | Specifies whether to enable |
WMM.| WMM. Only applies to bands B and G. Other bands will have it enabled regardless of this setting |
| wps-mode |
| (disabled | push-button | push-button-virtual-only; Default: |
...
802.11n wireless chipsets represent power per chain and the 802.11ac
802.11n wireless chipsets represent power per chain and the 802.11ac wireless chipsets represent the total power, for reference see the table below:Transmit Power representation on 802.11n and 802.11ac
Wireless chipset signal level representation
| Wireless chipset | Enabled Chains | Power per Chain | Total Power |
|---|
| 802.11n | 1 | Equal to the selected Tx Power | Equal to the selected Tx Power |
| 802.11n | 2 | Equal to the selected Tx Power | +3dBm |
| 802.11n | 3 | Equal to the selected Tx Power | +5dBm |
| 802.11ac | 1 | Equal to the selected Tx Power | Equal to the selected Tx Power |
| 802.11ac | 2 | -3dBm | Equal to the selected Tx Power |
| 802.11ac | 3 | -5dBm | Equal to the selected Tx Power |
| 802.11ac | 4 | -6dBm | Equal to the selected Tx Power |
Basic and MCS Rate table
Default basic and supported rates, depending on selected band
| band | basic rates | basic-HT-mcs | basic-VHT-mcs | VHT-mcs | HT-mcs | supported rates |
|---|
| 2.4ghz-b | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1-11 |
| 2.4ghz-onlyg | 6 | - | - | - | - | 1-11,6-54 |
| 2.4ghz-onlyn | 6 | 0-7 | - | - | 0-23 | 1-11,6-54 |
| 2.4ghz-b/g | 1-11 | - | - | - | - | 1-11,6-54 |
| 2.4ghz-b/g/n | 1-11 | none | - | - | 0-23 | 1-11,6-54 |
| 2.4ghz-g/n | 6 | none | - | - | 0-23 | 6-54 |
| 2.4ghz-g-turbo | 6 | - | - | - | - | 6-54 |
| 5ghz-a | 6 | - | - | - | - | 6-54 |
| 5ghz-a/n | 6 | none | - | - | 0-23 | 6-54 |
| 5ghz-onlyn | 6 | 0-7 | - | - | 0-23 | 6-54 |
| 5ghz-a/n/ac | 6 | none | none | 0-9 | 0-23 | 6-54 |
| 5ghz-onlyac | 6 | none | 0-7 | 0-9 | 0-23 | 6-54 |
...
802.11 standard provides means to protect the transmission against other device transmission by using RTS/CTS protocol. Frame protection helps to fight "hidden node" problem. There are several types of protection:
...
- Increased speed
- More client connections in PTM environments
- Lower latency
- No distance limitations
- No penalty for long distances
Starting from RouterOS v5.0beta5 you can configure Nv2 in the Wireless menu. Please take a look at the NV2 protocol implementation status. Nv2 protocol limit is 511 clients.
...
Access list is used by access point to restrict allowed connections from other devices, and to control connection parameters.Operation:
Access list rules are
...
processed one by one until matching rule is found. Then the action in the matching rule is
...
executed.
...
If action specifies that client should be accepted, client is accepted, potentially overriding it's default connection parameters with ones specified in access list rule.
There are the following parameters for access list rules:
- client matching parameters:
- address - MAC address of the client
- interface - optional interface to compare with the interface to which client actually connects to
- time - time of day and days when rule matches
- signal-range - range in which client signal must fit for the rule to match
- allow-signal-out-of-range - option which permits client's signal to be out of the range always or for some time interval
- connection parameters:
- ap-tx-limit - tx speed limit in direction to client
- client-tx-limit - tx speed limit in direction to AP (applies to RouterOS clients only)
- private-passphrase - PSK passphrase to use for this client if some PSK authentication algorithm is used
- vlan-mode - VLAN tagging mode specifies if traffic coming from client should get tagged (and untagged when going to client).
- vlan-id - VLAN ID to use if doing VLAN tagging
Operation:
- Access list rules are checked sequentially.
- Disabled rules are always ignored.
- Only the first matching rule is applied.
- If there are no matching rules for the remote connection, then the default values from the wireless interface configuration are used.
- If remote device is matched by rule that has authentication=no value, the connection from that remote device is rejected.
Warning: If there is no entry in ACL about client which connects to AP (wireless,debug wlan2: A0:0B:BA:D7:4D:B2 not in local ACL, by default accept), then ACL for this client is ignored during all connection time.
For example, if client's signal during connection is -41 and we have ACL rule
/interface/wireless/access-list
add authentication=yes forwarding=yes interface=wlan2 signal-range=-55..0
Then the connection is matched to the ACL rule, but if signal drops below -55, client will not be disconnected.
Please note that if "default-authentication=yes" is set on the wireless interface, clients will be able to join even if there are no matching access-list entries.
To make it work correctly it is required that client is matched by any of ACL rules.
If we modify ACL rules in the previous example to:
/interface/wireless/access-list
add interface=wlan2 signal-range=-55..0
add authentication=no forwarding=no interface=wlan2 signal-range=-120..-56
Then if signal drops to -56, client will be disconnected.
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|
| ap-tx-limit (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: 0) | Limit rate of data transmission to this client. Value 0 means no limit. Value is in bits per second. |
| authentication (yes | no; Default: yes) | - no - Client association will always fail.
- yes - Use authentication procedure that is specified in the security-profile of the interface.
|
| client-tx-limit (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: 0) | Ask client to limit rate of data transmission. Value 0 means no limit. This is a proprietary extension that is supported by RouterOS clients. Value is in bits per second. |
| comment (string; Default: ) | Short description of an entry |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) |
|
| forwarding (yes | no; Default: yes) | - no - Client cannot send frames to other station that are connected to same access point.
- yes - Client can send frames to other stations on the same access point.
|
| interface (string | any | all; Default: any) | Rules with interface=any are used for any wireless interface and the interface=all defines interface-list “all” name. To make rule that applies only to one wireless interface, specify that interface as a value of this property. |
| mac-address (MAC; Default: 00:00:00:00:00:00) | Rule matches client with the specified MAC address. Value 00:00:00:00:00:00 matches always. |
| management-protection-key (string; Default: "") |
|
| private-algo (104bit-wep | 40bit-wep | aes-ccm | none | tkip; Default: none) | Only for WEP modes. |
| private-key (string; Default: "") | Only for WEP modes. |
| private-pre-shared-key (string; Default: "") | Used in WPA PSK mode. |
| signal-range (NUM..NUM - both NUM are numbers in the range -120..120; Default: -120..120) | Rule matches if signal strength of the station is within the range. If signal strength of the station will go out of the range that is specified in the rule, access point will disconnect that station. |
| time (TIME-TIME,sun,mon,tue,wed,thu,fri,sat - TIME is time interval 0..86400 seconds; all day names are optional; value can be unset; Default: ) | Rule will match only during specified time. |
Warning: If there is no entry in ACL about client which connects to AP (wireless,debug wlan2: A0:0B:BA:D7:4D:B2 not in local ACL, by default accept), then ACL for this client is ignored during all connection time.
For example, if client's signal during connection is -41 and we have ACL rule
/interface wireless access-list
add authentication=yes forwarding=yes interface=wlan2 signal-range=-55..0
Then connection is not matched to any ACL rule and if signal drops to -70..-80, client will not be disconnected.
...
If we modify ACL rules in previous example to:
/interface wireless access-list
add interface=wlan2 signal-range=-55
add authentication=no forwarding=no interface=wlan2 signal-range=-120..-56
Then if signal drops to -56, client will be disconnected.
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|
| ap-tx-limit (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: 0) | Limit rate of data transmission to this client. Value 0 means no limit. Value is in bits per second. |
| authentication (yes | no; Default: yes) | - no - Client association will always fail.
- yes - Use authentication procedure that is specified in the security-profile of the interface.
|
| client-tx-limit (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: 0) | Ask client to limit rate of data transmission. Value 0 means no limit. This is a proprietary extension that is supported by RouterOS clients. Value is in bits per second. |
| comment (string; Default: ) | Short description of an entry |
disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | | forwarding (yes | no; Default: yes) | - no - Client cannot send frames to other station that are connected to same access point.
- yes - Client can send frames to other stations on the same access point.
|
| interface (string | any | all; Default: any) | Rules with interface=any are used for any wireless interface and the interface=all defines interface-list “all” name. To make rule that applies only to one wireless interface, specify that interface as a value of this property. |
| mac-address (MAC; Default: 00:00:00:00:00:00) | Rule matches client with the specified MAC address. Value 00:00:00:00:00:00 matches always. |
management-protection-key (string; Default: "") | | private-algo (104bit-wep | 40bit-wep | aes-ccm | none | tkip; Default: none) | Only for WEP modes. |
| private-key (string; Default: "") | Only for WEP modes. |
| private-pre-shared-key (string; Default: "") | Used in WPA PSK mode. |
| signal-range (NUM..NUM - both NUM are numbers in the range -120..120; Default: -120..120) | Rule matches if signal strength of the station is within the range. If signal strength of the station will go out of the range that is specified in the rule, access point will disconnect that station. |
| time (TIME-TIME,sun,mon,tue,wed,thu,fri,sat - TIME is time interval 0..86400 seconds; all day names are optional; value can be unset; Default: ) | Rule will match only during specified time. Station will be disconnected after specified time ends. Both start and end time is expressed as time since midnight, 00:00. Rule will match only during specified days of the week. |
...
connect-list is used to assign priority and security settings to connections with remote access points, and to restrict allowed connections. connect-list is an ordered list of rules. Each rule in connect-list is attached to specific wireless interface, specified in the interfaceproperty of that rule (this is unlike access-list, where rules can apply to all interfaces). Rule can match MAC address of remote access point, it's signal strength and many other parameters.
...
| Property | Description |
|---|
| 3gpp (string; Default: ) |
|
| area-prefix (string; Default: ) | Rule matches if area value of AP (a proprietary extension) begins with specified value.area value is a proprietary extension. |
| comment (string; Default: ) | Short description of an entry |
| connect (yes | no; Default: yes) | Available options:- yes - Connect to access point that matches this rule.
- no - Do not connect to any access point that matches this rule.
|
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) |
|
| mac-address (MAC; Default: 00:00:00:00:00:00) | Rule matches only AP with the specified MAC address. Value 00:00:00:00:00:00 matches always. |
| security-profile (string | none; Default: none) | Name of security profile that is used when connecting to matching access points, If value of this property is none, then security profile specified in the interface configuration will be used. In station mode, rule will match only access points that can support specified security profile. Value none will match access point that supports security profile that is specified in the interface configuration. In access point mode value of this property will not be used to match remote devices. |
| signal-range (NUM..NUM - both NUM are numbers in the range -120..120; Default: -120..120) | Rule matches if signal strength of the access point is within the range. If station establishes connection to access point that is matched by this rule, it will disconnect from that access point when signal strength goes out of the specified range. |
| ssid (string; Default: "") | Rule matches access points that have this SSID. Empty value matches any SSID. This property has effect only when station mode interface ssid is empty, or when access point mode interface has wds-ignore-ssid=yes |
| wireless-protocol (802.11 | any | nstreme | tdma; Default: any) |
|
| interface (string; Default: ) | Each rule in connect list applies only to one wireless interface that is specified by this setting. |
...
| Property | Description |
|---|
| 2ghz-10mhz-power-channels () |
|
| 2ghz-11n-channels () |
|
| 2ghz-5mhz-power-channels () |
|
| 2ghz-b-channels () |
|
| 2ghz-g-channels () |
|
| 2ghz-g-turbo-channels () |
|
| 5ghz-10mhz-power-channels () |
|
| 5ghz-11n-channels () |
|
| 5ghz-5mhz-power-channels () |
|
| 5ghz-channels () |
|
| 5ghz-turbo-channels () |
|
| allowed-channels | List of available channels for each band |
| capabilities () |
|
chip| country-info | () | Takes country name as argument, shows available bands, frequencies and maximum transmit power for each frequency. |
| chip-info () |
|
| default-periodicdefault-periodic-calibration () |
|
| firmware () |
|
| ht-chains () |
|
| interface-type () |
|
| name () |
|
| pci-info () |
|
| supported-bands () |
|
...
Warning: You must follow to regulatory domain requirements in your country. If you are allowed to use other frequencies, note that Antenna Gain and Transmit Power may decrease depending on board and frequency. Devices are calibrated only for regulatory frequencies, use non standard frequencies at your own risk. The list only specifies frequencies accepted by the wireless chip, these frequencies might not always work due to antenna that is built into the product, device design, filters and other factors. USE STRICTLY AT YOUR OWN RISK
Integrated wireless interface frequency table
It is possible to deduce supported channel width from the product page, to do so you need to check the following parameters: number of chains and the max data rate. Once you know these parameters, you need to check the modulation and coding scheme (MCS) table, for example, here: https://mcsindex.com/.
If we take hAP ac, as an example, we can see that number of chains is 3, and the max data rate is 1300 in the MCS table. In the MCS table we need to find entry for 3 spatial streams - chains, and the respective data rate, which in this case shows us that 80MHz is the maximum supported channel width.
Integrated wireless interface frequency table
| Board name | Wireless interfaces | Frequency range [MHz] | Supported channel widths [Mhz] |
|---|
| 2011UAS-2HnD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| 751G-2HnD | 1 | 2200-2700 | 20,40 and advanced channel support |
| 751U-2HnD | 1 | 2200-2700 | 20,40 and advanced channel support |
| 911-2Hn |
| Board name | Wireless interfaces | Frequency range [MHz] | Supported channel widths [Mhz] |
|---|
| 2011UAS-2HnD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| 751G-2HnD | 1 | 2200-2700 | 20,40 and advanced channel support |
| 751U-2HnD | 1 | 2200-2700 | 20,40 and advanced channel support |
| 911-2Hn | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| 911-5HacD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40,80 |
| 911-5Hn | 1 | 4920-6100 | 5,10,20,40 |
| 911-5HnD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40 |
| 911G-2HPnD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| 911-5HacD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40,80 |
| 911-5Hn | 1 | 4920-6100 | 5,10,20,40 |
| 911-5HnD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40 |
| 911G-2HPnD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| 911G-5HPacDr2 /-911G-5HPacD /-NB /-QRT | 1 | 4920-6100 | 5,10,20,40,80 |
| 911G-5HPnD /-QRT | 1 | 4920-6100 | 5,10,20,40 |
| 912UAG-2HPnD /-OUT | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| 912UAG-5HPnD /-OUT | 1 | 4920-6100 | 5,10,20,40 |
| 912UAG-6HPnD /-OUT | 1 | 5500-6500 | and 20,40 |
| 921GS-5HPacD-15S /-19S | 1 | 4920-6100 | 51,101,20,40,80 |
| 22UGS-5HPacD2HnD | 2 | 4920-5925,2412-2482 | 20,40,80 and 20,40 |
| 921UAGS-5SHPacD-NM | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40,80 |
| 921UAGS-5SHPacT-NM | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40,80 |
| 922UAGS-5HPacD /-NM | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40,80 |
| 922UAGS-5HPacT /-NM | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40,80 |
| 941-2nD /-TC | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| 951G-2HnD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| 951Ui-2HnD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| 951Ui-2nD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| 952Ui-5ac2nD /-TC | 2 | 2312-2732,4920-6100 | 20,40 and 20,40,80 |
| 953GS-5HnT /-RP | 1 | 4920-6100 | 5,10,20,40 |
| 962UiGS-5HacT2HnT | 2 | 2312-2732,4920-6100 | 20,40 and 20,40,80 |
| cAP2n | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| cAP2nD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| cAPL-2nD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| CRS109-8G-1S-2HnD-IN | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| CRS125-24G-1S-2HnD-IN | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| Disc-5nD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40 |
| DynaDishG-5HacD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 51,101,20,40,80 |
| DynaDishG-6HnD | 1 | 5500-6500 | 20,40 |
| Groove52HPn | 1 | 4920-6100,2312-2732 | 5,10,20,40 and 5,10,20,40 |
| GrooveA-52HPn | 1 | 4920-6100,2312-2732 | 5,10,20,40 and 5,10,20,40 |
| GrooveG-52HPacn | 1 | 4920-6100,2312-2732 | 20,40,80 and 20,40 |
| GrooveGA-52HPacn | 1 | 4920-6100,2312-2732 | 20,40,80 and 20,40 |
| LDF-5nD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40 |
| LHG-5nD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40 |
| mAP2n | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| mAP2nD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| mAPL-2nD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| Metal2SHPn | 1 | 2200-2700 | 20,40 and advanced channel support |
| Metal5SHPn | 1 | 4800-6100 | 5,10,20,40 and advanced channel support |
| Metal9HPn | 1 | 902-928 | 5,10,20 |
| MetalG-52SHPacn | 1 | 4920-6100,2312-2732 | 20,40,80 and 20,40 |
| OmniTikG-5HacD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40,80 |
| OmniTikPG-5HacD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40,80 |
| OmniTIKU-5HnD | 1 | 4800-6100 | 5,10,20,40 |
| OmniTIKUPA-5HnD | 1 | 4800-6100 | 5,10,20,40 |
| QRTG-2SHPnD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| SEXTANTG-5HPnD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40 |
| SXT2nDr2 | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| SXT5HacD2n | 2 | 2312-2732,4920-6100 | 51,101,20,40 and 51,101,20,40,80 |
| SXT5HPnDr2 | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40 |
| SXT5nDr2 | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40 |
| SXTG-2HnD | 1 | 2200-2700 | 20,40 |
| SXTG-2HnDr2 | 1 | 2300-2700 | 20,40 |
| SXTG-5HPacD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 51,101,20,40,80 |
| SXTG-5HPacD-HG /-SA | 1 | 4920-6100 | 51,101,20,40,80 |
| SXTG-5HPnD-HGr2 /-SAr2 | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40 |
| SXTG-6HPnD | 1 | 5500-6500 | 20,40 |
| SXTsq2nD | 1 | 2312-2484 | 20,40 |
| wAP2nD /-BE | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| wAPG-5HacT2HnD /-BE | 2 | 2312-2732,4920-6100 | 20,40 and 20,40,80 |
| R11e-2HnD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| R11e-2HPnD | 1 | 2312-2732 | 20,40 |
| R11e-5HacD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40,80 |
| R11e-5HacT | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40,80 |
| R11e-5HnD | 1 | 4920-6100 | 20,40 |
| R2SHPn | 1 | 2200-2700 | 20,40 and advanced channel support |
| R52H | 1 | 4920-6100,2192-2507 | 20 and 20 |
| R52HnD | 1 | 4800-6100,2200-2700 | 20,40 and 20,40 |
| R52nM | 1 | 4800-6100,2200-2700 | 20,40 and 20,40 and advanced channel support |
| R5SHPn | 1 | 4800-6100 | 20,40 and advanced channel support |
NOTES:
...
|
| R52HnD | 1 | 4800-6100,2200-2700 | 20,40 and 20,40 |
| R52nM | 1 | 4800-6100,2200-2700 | 20,40 and 20,40 and advanced channel support |
| R5SHPn | 1 | 4800-6100 | 20,40 and advanced channel support |
NOTES:
- - Only in 802.11a/n standard
Overview
Advanced Channels feature provides extended opportunities in wireless interface configuration:
- scan-list that covers multiple bands and channel widths;
- non-standard channel center frequencies (specified with KHz granularity) for hardware that allows that;
- non-standard channel widths (specified with KHz granularity) for hardware that allows that.
Hardware support
Non standard center frequency and width channels can only be used with interfaces that support it.
Currently only Atheros AR92xx based chips support non-standard center frequencies and widths with the following ranges:
- center frequency range: 2200MHz-2500MHz with step 0.5MHz (500KHz), width range: 2.5MHz-30MHz width step 0.5MHz (500KHz);
- center frequency range: 4800MHz-6100MHz with step 0.5MHz (500KHz), width range: 2.5MHz-30MHz width step 0.5MHz (500KHz);
AR93xx doesn't support this feature
Configuring Advanced Channels
Advanced Channels are configured in interface wireless channels menu. This menu contains ordered list of user-defined channels that can be grouped by means of list property. Channels have the following properties:
- name - name by which this channel can be referred to. If name is not specified when adding channel, it will be automatically generated from channel frequency and width;
- list - name of list this channel is part of. Lists can be used to group channels;
- frequency - channel center frequency in MHz, allowing to specify fractional MHz part, e.g. 5181.5;
- width - channel width in MHz, allowing to specify fractional MHz part, e.g. 14.5;
- band - defines default set of data rates when using this channel;
- extension-channel - specifies placement of 11n extension channel.
Using Advanced Channels
In order to use Advanced Channels in wireless interface configuration, several interface settings accept channel names or list names as arguments. It is possible to configure interface with channel that interface does not support. In this case interface will not become operational. It is sole responsibility of administrator to configure channels in proper way.
frequency
To use particular Advanced Channel for wireless interface (applies to modes that make use of interface frequency setting) specify channel name in interface frequency setting. For example, to configure interface to operate with center frequency 5500MHz and channel width 14MHz, use the following commands:
[admin@MikroTik] /interface wireless> channels add name=MYCHAN frequency=5500 width=14 band=5ghz-onlyn
list=MYLIST
[admin@MikroTik] /interface wireless> set wlan1 frequency=MYCHAN
scan-list
Interface scan-list is used in multiple modes that either gather information for list of channels (like interactive scan command) or selects channel to work on (like any of station modes or AP modes performing DFS). Interface scan-list can be configured with comma-separated list of the following items:
- default - default .11 channel list for given country and interface band and channel width;
- numeric frequency ranges in MHz;
- Advanced Channel, referred to by name;
- Advanced Channel list, referred to by list name.
For example, to configure interface to scan 5180MHz, 5200MHz and 5220MHz at first using channel width 20MHz and then using channel width 10MHz, the following commands can be issued:
[admin@MikroTik] /interface wireless> channels add frequency=5180 width=20 band=5ghz-a list=20MHz-list
[admin@MikroTik] /interface wireless> channels add frequency=5200 width=20 band=5ghz-a list=20MHz-list
[admin@MikroTik] /interface wireless> channels add frequency=5220 width=20 band=5ghz-a list=20MHz-list
[admin@MikroTik] /interface wireless> channels add frequency=5180 width=10 band=5ghz-a list=10MHz-list
[admin@MikroTik] /interface wireless> channels add frequency=5200 width=10 band=5ghz-a list=10MHz-list
[admin@MikroTik] /interface wireless> channels add frequency=5220 width=10 band=5ghz-a list=10MHz-list
[admin@MikroTik] /interface wireless> set wlan1 scan-list=20MHz-list,10MHz-list
Nstreme
Sub-menu: /interface wireless nstreme
...
| Property | Description |
|---|
| 802.1x-port-enabled (yes | no) | whether the data exchange is allowed with the peer (i.e., whether 802.1x authentication is completed, if needed) |
| ack-timeout (integer) | current value of ack-timeout |
| ap (yes | no) | Shows whether registered device is configured as access point. |
| ap-tx-limit (integer) | transmit rate limit on the AP, in bits per second |
| authentication-type () | authentication method used for the peer |
| bridge (yes | no) |
|
| bytes (integer , integer) | number of sent and received packet bytes |
| client-tx-limit (integer) | transmit rate limit on the AP, in bits per second |
| comment (string) | Description of an entry. comment is taken from appropriate Access List entry if specified. |
| compression (yes | no) | whether data compresson is used for this peer |
| distance (integer) |
|
| encryption (aes-ccm | tkip) | unicast encryption algorithm used |
| evm-ch0 () |
|
| evm-ch1 () |
|
| evm-ch2 () |
|
| frame-bytes (integer,integer) | number of sent and received data bytes excluding header information |
| frames (integer,integer) | Number of frames that need to be sent over wireless link. This value can be compared to hw-frames to check wireless retransmits. Read more >> |
| framing-current-size (integer) | current size of combined frames |
| framing-limit (integer) | maximal size of combined frames |
| framing-mode () | the method how to combine frames |
| group-encryption () | group encryption algorithm used |
| hw-frame-bytes (integer,integer) | number of sent and received data bytes including header information |
| hw-frames (integer,integer) | Number of frames sent over wireless link by the driver. This value can be compared to frames to check wireless retransmits. Read more >> |
| interface (string) | Name of the wireless interface to which wireless client is associated |
| last-activity (time) | last interface data tx/rx activity |
| last-ip (IP Address) | IP address found in the last IP packet received from the registered client |
| mac-address (MAC) | MAC address of the registered client |
| management-protection (yes | no) |
|
| nstreme (yes | no) | Shows whether Nstreme is enabled |
| p-throughput (integer) | estimated approximate throughput that is expected to the given peer, taking into account the effective transmit rate and hardware retries. Calculated once in 5 seconds |
| packed-bytes (integer, integer) | number of bytes packed into larger frames for transmitting/receiving (framing) |
| packed-frames (integer, integer) | number of frames packed into larger ones for transmitting/receiving (framing) |
| packets (integer.integer) | number of sent and received network layer packets |
| radio-name (string) | radio name of the peer |
| routeros-version (string) | RouterOS version of the registered client |
| rx-ccq () | Client Connection Quality (CCQ) for receive. Read more >> |
| rx-rate (integer) | receive data rate |
| signal-strength (integer) | average strength of the client signal recevied by the AP |
| signal-strength-ch0 () |
|
| signal-strength-ch1 () |
|
| signal-strength-ch2 () |
|
| signal-to-noise () |
|
| strength-at-rates () | signal strength level at different rates together with time how long were these rates used |
| tdma-retx () |
|
| tdma-rx-size () |
|
| tdma-timing-offset () | tdma-timing-offset is proportional to distance and is approximately two times the propagation delay. AP measures this so that it can tell clients what offset to use for their transmissions - clients then subtract this offset from their target transmission time such that propagation delay is accounted for and transmission arrives at AP when expected. You may occasionally see small negative value (like few usecs) there for close range clients because of additional unaccounted delay that may be produced in transmitter or receiver hardware that varies from chipset to chipset. |
| tdma-tx-size (integer) | Value in bytes that specifies the size of data unit whose loss can be detected (data unit over which CRC is calculated) sent by device. In general - the bigger the better, because overhead is less. On the other hand, small value in this setting can not always be considered a signal that connection is poor - if device does not have enough pending data that would enable it to use bigger data units (e.g. if you are just pinging over link), this value will not go up. |
| tdma-windfull () |
|
| tx-ccq () | Client Connection Quality (CCQ) for transmit. Read more >> |
| tx-evm-ch0 () |
|
| tx-evm-ch1 () |
|
| tx-evm-ch2 () |
|
| tx-frames-timed-out () |
|
| tx-rate () |
|
| tx-signal-strength () |
|
| tx-signal-strength-ch0 () |
|
| tx-signal-strength-ch1 () |
|
| tx-signal-strength-ch2 () |
|
| uptime (time) | time the client is associated with the access point |
| wds (yes | no) | whether the connected client is using wds or not |
| wmm-enabled (yes | no) | Shows whether WMM is enabled. |
Security Profiles
Sub-menu: /interface wireless security-profiles
Security profiles are configured under the /interface wireless security-profiles path in the console, or in the "Security Profiles" tab of the "Wireless" window in the WinBox. Security profiles are referenced by the Wireless interface security-profile property and security-profile property of Connect Lists.
...
| Property | Description |
|---|
| mode (none | static-keys-optional | static-keys-required | dynamic-keys; Default: none) | Encryption mode for the security profile.- none - Encryption is not used. Encrypted frames are not accepted.
- static-keys-required - WEP mode. Do not accept and do not send unencrypted frames. Station in static-keys-required mode will not connect to an Access Point in static-keys-optional mode.
- static-keys-optional - WEP mode. Support encryption and decryption, but allow also to receive and send unencrypted frames. Device will send unencrypted frames if encryption algorithm is specified as none. Station in static-keys-optional mode will not connect to an Access Point in static-keys-required mode. See also: static-sta-private-algo, static-transmit-key.
- dynamic-keys - WPA mode.
|
| name (text; Default: ) | Name of the security profile |
...
| Property | Description |
|---|
| authentication-types (wpa-psk | wpa2-psk | wpa-eap | wpa2-eap; Default: ) | Set of supported authentication types, multiple values can be selected. Access Point will advertise supported authentication types, and client will connect to Access Point only if it supports any of the advertised authentication types. |
| disable-pmkid (no | yes; Default: no) | Whether to include PMKID into the EAPOL frame sent out by the Access Point. Disabling PMKID can cause compatibility issues with devices that use the PMKID to connect to an Access Point.- yes - removes PMKID from EAPOL frames (improves security, reduces compatibility).
- no - includes PMKID into EAPOL frames (reduces security, improves compatibility).
This property only has effect on Access Points. |
| unicast-ciphers (tkip | aes-ccm; Default: aes-ccm) | Access Point advertises that it supports specified ciphers, multiple values can be selected. Client attempts connection only to Access Points that supports at least one of the specified ciphers. One of the ciphers will be used to encrypt unicast frames that are sent between Access Point and Station. |
| group-ciphers (tkip | aes-ccm; Default: aes-ccm) | Access Point advertises one of these ciphers, multiple values can be selected. Access Point uses it to encrypt all broadcast and multicast frames. Client attempts connection only to Access Points that use one of the specified group ciphers.- tkip - Temporal Key Integrity Protocol - encryption protocol, compatible with legacy WEP equipment, but enhanced to correct some of the WEP flaws.
- aes-ccm - more secure WPA encryption protocol, based on the reliable AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). Networks free of WEP legacy should use only this cipher.
|
| group-key-update (time: 30s..1h1d; Default: 5m) | Controls how often Access Point updates the group key. This key is used to encrypt all broadcast and multicast frames. property only has effect for Access Points. |
| wpa-pre-shared-key (text; Default: ) | WPA pre-shared key mode requires all devices in a BSS to have common secret key. Value of this key can be an arbitrary text. Commonly referred to as the network password for WPA mode. property only has effect when wpa-psk is added to authentication-types. |
| wpa2-pre-shared-key (text; Default: ) | WPA2 pre-shared key mode requires all devices in a BSS to have common secret key. Value of this key can be an arbitrary text. Commonly referred to as the network password for WPA2 mode. property only has effect when wpa2-psk is added to authentication-types. |
Note: RouterOS also allows to override pre-shared key value for specific clients, using either the private-pre-shared-key property, or the Mikrotik-Wireless-Psk attribute in the RADIUS MAC authentication response. This is an extension.
...
| Property | Description |
|---|
| eap-methods (eap-tls | eap-ttls-mschapv2 | passthrough | peap; Default: passthrough) | Allowed types of authentication methods, multiple values can be selected. This property only has effect on Access Points.- eap-tls - Use built-in EAP TLS authentication. Both client and server certificates are supported. See description of tls-mode and tls-certificate properties.
- eap-ttls-mschapv2 - Use EAP-TTLS with MS-CHAPv2 authentication.
- passthrough - Access Point will relay authentication process to the RADIUS server.
- peap - Use Protected EAP authentication.
|
| supplicant-identity (text; Default: Identity) | EAP identity that is sent by client at the beginning of EAP authentication. This value is used as a value for User-Name attribute in RADIUS messages sent by RADIUS EAP accounting and RADIUS EAP pass-through authentication. |
| mschapv2-username (text; Default: ) | Username to use for authentication when eap-ttls-mschapv2 or peap authentication method is being used. This property only has effect on Stations. |
| mschapv2-password (text; Default: ) | Password to use for authentication when eap-ttls-mschapv2mschapv2 or peap authentication method is being used. This property only has effect on Stations. |
| tls-mode (verify-certificate | dont-verify-certificate | no-certificates | verify-certificate-with-crl; Default: no-certificates) | This property has effect only when eap-methods contains eap-tls.- verify-certificate - Require remote device to have valid certificate. Check that it is signed by known certificate authority. No additional identity verification is done. Certificate may include information about time period during which it is valid. If router has incorrect time and date, it may reject valid certificate because router's clock is outside that period. See also the Certificates configuration.
- dont-verify-certificate - Do not check certificate of the remote device. Access Point will not require client to provide certificate.
- no-certificates - Do not use certificates. TLS session is established using 2048 bit anonymous Diffie-Hellman key exchange.
- verify-certificate-with-crl - Same as verify-certificate but also checks if the certificate is valid by checking the Certificate Revocation List.
|
| tls-certificate (none | name; Default: none) | Access Point always needs a certificate when configured when tls-mode is set to verify-certificate, or is set to dont-verify-certificate. Client needs a certificate only if Access Point is configured with tls-mode set to verify-certificate. In this case client needs a valid certificate that is signed by a CA known to the Access Point. This property only has effect when tls-mode is not set to no-certificates and eap-methods contains eap-tls. |
...
RADIUS properties
| Property | Description |
|---|
| radius-mac-authentication (yes | no; Default: no) | This property affects the way how Access Point processes clients that are not found in the Access List.- no - allow or reject client authentication based on the value of default-authentication property of the Wireless interface.
- yes - Query RADIUS server using MAC address of client as user name. With this setting the value of default-authentication has no effect.
|
| radius-mac-accounting (yes | no; Default: no) |
|
| radius-eap-accounting (yes | no; Default: no) |
|
| radius-called-format (mac | mac:ssid | ssid; Default: mac:ssid) |
|
| interim-update (time; Default: 0) | When RADIUS accounting is used, Access Point periodically sends accounting information updates to the RADIUS server. This property specifies default update interval that can be overridden by the RADIUS server using Acct-Interim-Interval attribute. |
| radius-mac-format (XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX | XXXX:XXXX:XXXX | XXXXXX:XXXXXX | XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX | XXXXXX-XXXXXX | XXXXXXXXXXXX | XX XX XX XX XX XX | lower case; Default: XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX) | Controls how MAC address of the client is encoded by Access Point in the User-Name attribute of the MAC authentication and MAC accounting RADIUS requests. |
| radius-mac-mode (as-username | as-username-and-password; Default: as-username) | By default Access Point uses an empty password, when sending Access-Request during MAC authentication. When this property is set to as-username-and-password, Access Point will use the same value for User-Password attribute as for the User-Name attribute. |
| radius-mac-caching (disabled | time; Default: disabled) | If this value is set to time interval, the Access Point will cache RADIUS MAC authentication responses for specified time, and will not contact RADIUS server if matching cache entry already exists. Value disabled will disable cache, Access Point will always contact RADIUS server. |
...
| Property | Description |
|---|
| static-key-0 | static-key-1 | static-key-2 | static-key-3 (hex; Default: ) | Hexadecimal representation of the key. Length of key must be appropriate for selected algorithm. See the Statically configured WEP keys section. |
| static-algo-0 | static-algo-1 | static-algo-2 | static-algo-3 (none | 40bit-wep | 104bit-wep | tkip | aes-ccm; Default: none) | Encryption algorithm to use with the corresponding key. |
| static-transmit-key (key-0 | key-1 | key-2 | key-3; Default: key-0) | Access Point will use the specified key to encrypt frames for clients that do not use private key. Access Point will also use this key to encrypt broadcast and multicast frames. Client will use the specified key to encrypt frames if static-sta-private-algo is set to none. If corresponding static-algo-N property has value set to none, then frame will be sent unencrypted (when mode is set to static-keys-optional) or will not be sent at all (when mode is set to static-keys-required). |
| static-sta-private-key (hex; Default: ) | Length of key must be appropriate for selected algorithm, see the Statically configured WEP keys section. This property is used only on Stations. Access Point uses corresponding key either from private-key property, or from Mikrotik-Wireless-Enc-Key attribute. |
| static-sta-private-algo (none | 40bit-wep | 104bit-wep | tkip | aes-ccm; Default: none) | Encryption algorithm to use with station private key. Value none disables use of the private key. This property is only used on Stations. Access Point has to get corresponding value either from private-algo property, or from Mikrotik-Wireless-Enc-Algo attribute. Station private key replaces key 0 for unicast frames. Station will not use private key to decrypt broadcast frames. |
...
[admin@mikrotik] /interface wireless security-profiles> set default management-protection=
allowed disabled required
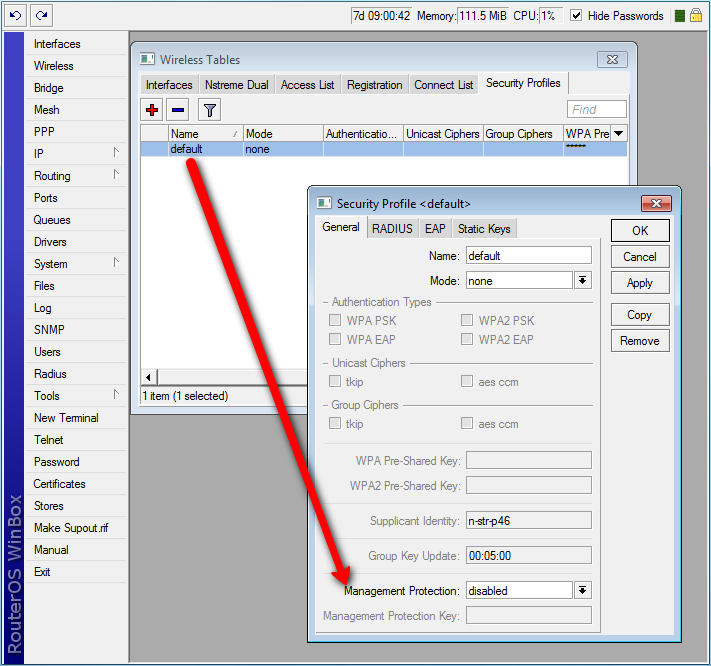 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
Operation details
...
Note: RAIDUS MAC authentication is used by access point for clients that are not found in the access-list, similarly to the default-authentication property of the wireless interface. It controls whether client is allowed to proceed with authentication, or is rejected immediately.
...
- Ascend-Data-Rate
- Ascend-Xmit-Rate
- Mikrotik-Wireless-Forward - Same as access-list forwarding.
- Mikrotik-Wireless-Enc-Algo - Same as access-list private-algo.
- Mikrotik-Wireless-Enc-Key - Same as access-list private-key.
- Mikrotik-Wireless-Psk - Same as access-list private-pre-shared-key.
- Mikrotik-Wireless-Mpkey - Same as Management-protection-key in Access list
- Session-Timeout - Time, after which client will be disconnected.
- Acct-Interim-Interval - Overrides value of interim-update.
- Class - If present, value of this attribute is saved and included in Accounting-Request messages.
...
- User-Name - EAP supplicant identity. This value is configured in the supplicant-identity property of the client security profile.
- Nas-Port-Id - name of wireless interface.
- Calling-Station-Id - Client MAC address, encoded as "XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX".
- Called-Station-Id - MAC address and SSID of the access point, encoded as "XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX:SSID" (pairs of MAC address digits separated by minus sign, followed by colon, followed by SSID value).
- Acct-Session-Id - Added when radius-eap-accounting=yes.
- Acct-Multi-Session-Id - MAC address of access point and client, and unique 8 byte value, that is shared for all accounting sessions that share single EAP authentication. Encoded as AA-AA-AA-AA-AA-AA-CC-CC-CC-CC-CC-CC-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX. Added
...
- when radius-eap-accounting=yes.
Access point uses following RADIUS attributes from the Access-Accept server response:
...
It is possible to use one security profile for all clients, and different security profiles for WDS links. Security profile for WDS link is specified in connect-list. Access point always checks connect list before establishing WDS link with another access point, and used security settings from matching connect list entry. WDS link will work when each access point will have connect list entry that matches the other device, has connect=yes and specifies compatible security-profile.
...
Security profile and access point matching in the connect list
Client uses value of connect-list security-profile property to match only those access points that support necessary security.
...
| Property | Description |
|---|
| channel-time (; Default: 200ms)) | How long to sniff each channel. Used only if multiple-channels=yes |
| file-limit (integer [10..4294967295]; Default: 10) | Allocated file size in bytes which will be used to store captured data. Applicable if file-name is specified. |
| file-name (string; Default: ) | Name of the file where to store captured data. |
| memory-limit (integer [10..4294967295]; Default: 10) | Allocated memory buffer in bytes kilobytes used to store captured data. |
| multiple-channels (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to sniff multiple channels or a single channel. No means that all channel settings will be taken from /interface wireless,
Yes means that all channel settings will be taken from scan-list under /interface wireless. |
| only-headers (yes | no; Default: no) | If set to yes, then sniffer will capture only information stored in frame headers. |
| receive-errors (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to process packets which have been received with errors judging by their FCS. |
| streaming-enabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to stream captured data to the specified streaming server |
| streaming-max-rate (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: 0) | Maximum packets per second allowed. 0 equals unlimited |
| streaming-server (IPv4; Default: 0.0.0.0) | IP address of the streaming server. |
| Info |
|---|
Use the command /interface wireless info scan-list to verify your scan-list defined under /interface wireless channels when using multiple-channels=yes |
Packets
Sub-menu: /interface wireless sniffer packet
...
This tool monitors surrounding frequency usage, and displays which devices occupy each frequency. It's available both in console, and also in Winbox. Snooper will use frequencies from scan-list.
Sub-menu: /interface wireless snooper
 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
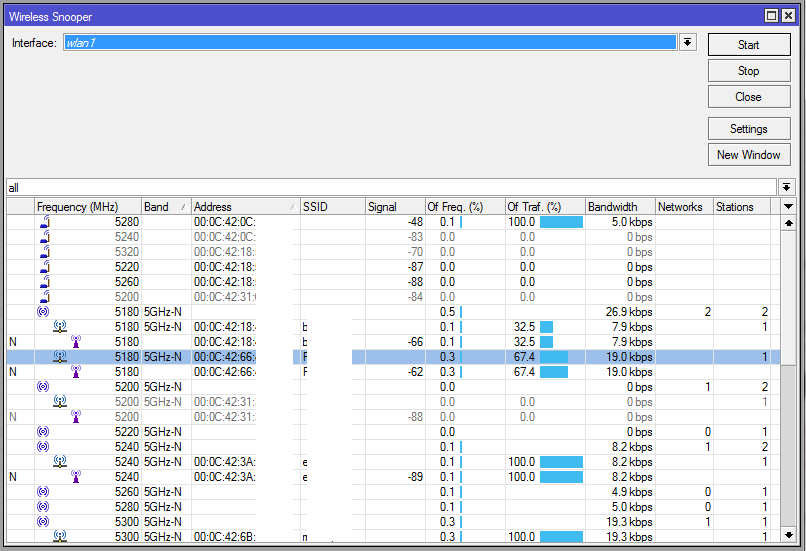 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
Settings
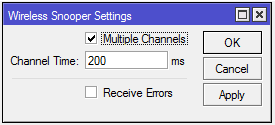 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
Spectral scan
- See separate document Manual:Spectral_scan
...
- address - MAC address of AP to setup repeater for (optional)
- ssid - SSID of AP to setup repeater for (optional)
- passphrase - key to use for AP - if this IS specified, command will just scan for AP and create security profile based on info in beacon and with this passphrase. If this IS NOT specified, command will do WPS to find out passphrase.
The same options are available in the GUI:
...
Roaming
Station Roaming
Station Roaming feature is available only for 802.11 wireless protocol and only for station modes. When RouterOS wireless client is connected to the AP using 802.11 wireless protocol it will periodically perform the background scan with specific time intervals. When the background scan will find an AP with better signal it will try to roam to that AP. The time intervals between the background scans will become shorter when the wireless signal becomes worse and the background scan interval will become longer when the wireless client signal will get better.
...
This way traffic can be separated between wireless clients even on the same interface, but must be used with care - only "interface VLAN" broadcast/multicast traffic will be sent out. If working broadcast/multicast is necessary for other (overridden) VLANs as well, multicast-helper can be used for now (this changes every multicast packet to unicast and then it is only sent to clients with matching VLAN ids).
Winbox
Winbox is a small utility that allows the administration of Mikrotik RouterOS using a fast and simple GUI.
...
Interworking Realms setting
Starting from RouterOS v6.42rc27 we have added such feature:For more information about interworking-profiles see the manual.
realms-raw - list of strings with hex values. Each string specifies contents of "NAI Realm Tuple", excluding "NAI Realm Data Field Length" field.
...







